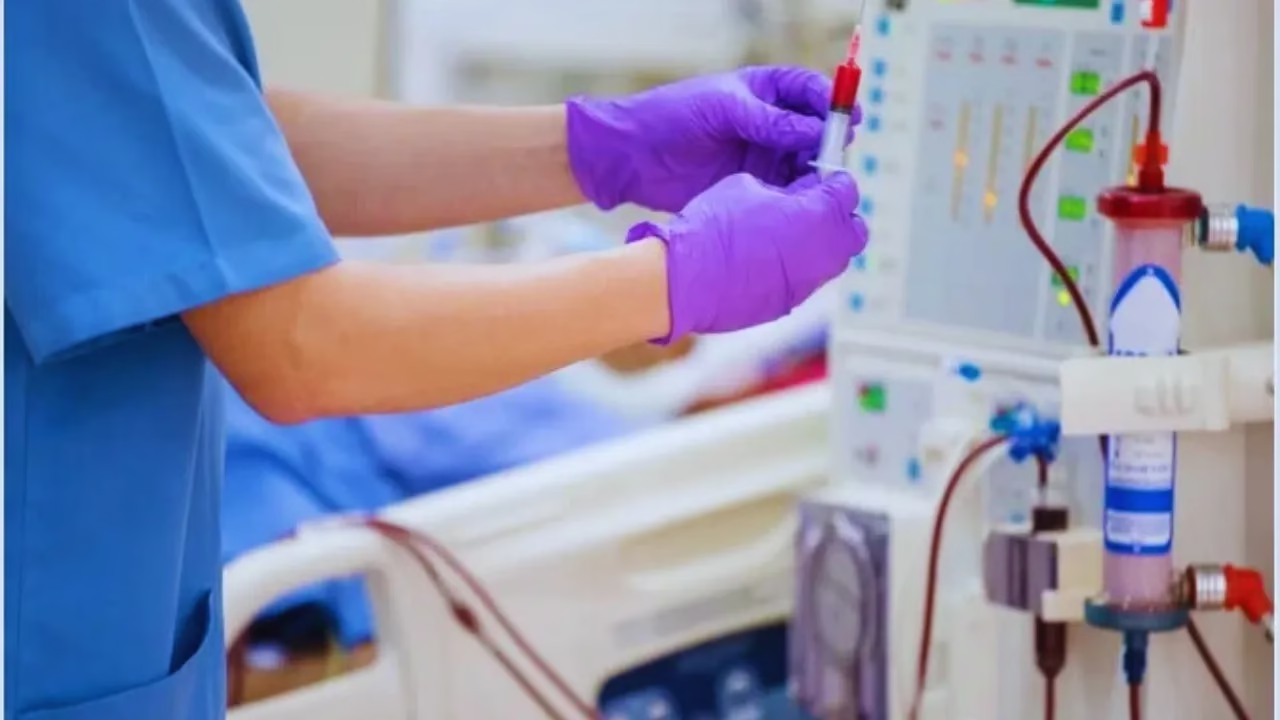
Renal dialysis technology has revolutionized the way we manage kidney failure and related disorders, offering hope and extended life to millions of individuals around the globe. As kidney diseases continue to rise, innovations in dialysis are becoming increasingly vital. I will dive deep into the modern landscape of renal dialysis technology, how it is transforming treatment outcomes, and the various advanced tools shaping patient care.
From high-performance machines in hospitals to wearable home-based systems, dialysis technology has evolved to meet the demands of a growing patient population. These technologies not only aim to replicate kidney function but also enhance patient comfort, reduce treatment time, and minimize hospital visits. These advancements is crucial for patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals as they navigate options for long-term kidney support.
Comparing Types of Renal Dialysis Technologies
Technology has diversified renal dialysis options, allowing for tailored treatments based on a patient’s condition and lifestyle. The primary methods include hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and home-based systems. Each technology offers unique advantages, depending on the patient’s medical requirements and convenience.
| Technology Type | Location of Treatment | Main Equipment Used | Frequency | Suitable For |
| Hemodialysis | Hospital or Dialysis Center | Dialyzer, Dialysis Machine | 3 times a week | Patients needing clinical monitoring |
| Peritoneal Dialysis | Home | Catheter, Dialysate Bags | Daily (multiple exchanges) | Active patients needing flexibility |
| Home Hemodialysis | Home | Portable Dialysis Machine | 5–6 times a week | Patients preferring independence |
| Nocturnal Hemodialysis | Home | Advanced Dialysis Machine | Overnight, daily | Stable patients seeking comfort |
These approaches highlight the versatility and adaptability of current renal dialysis technologies to accommodate patient preferences, availability, and health conditions.
Modern Innovations in Dialysis Devices
Today’s renal dialysis machines are significantly more advanced than earlier models. They feature compact designs, making them easier to install and manage in various settings. Modern machines prioritize user-friendly interfaces for both patients and caregivers. Remote connectivity allows for real-time data sharing and better clinical oversight. Automated peritoneal dialysis (PD) systems reduce manual effort during treatment.
Wearable dialysis devices now offer mobility and freedom during therapy sessions. Integrated sensors provide real-time feedback on blood pressure and fluid balance. These systems alert users and healthcare providers in case of irregularities. Such innovations minimize treatment disruptions and enhance overall efficiency. As a result, patients experience better safety, comfort, and long-term outcomes.
Clinical Applications and Patient Outcomes
Renal dialysis technology doesn’t merely act as a temporary solution; it has become an integral part of managing end-stage renal disease (ESRD). By replicating kidney functions externally, dialysis helps maintain electrolyte balance, remove waste products, and manage fluid levels. The incorporation of advanced sensors, artificial intelligence, and integrated alert systems has made monitoring and emergency response quicker and more accurate.
| Advancement | Patient Benefit | Clinical Outcome |
| Automated Fluid Management | Prevents dehydration and overload | Stable hemodynamic performance |
| AI-Powered Dialysis | Adjusts parameters in real time | Reduced complications |
| Portable Machines | Facilitates home and travel use | Improved treatment adherence |
| Infection Control Systems | Uses UV and filtration for sterilization | Fewer infections and hospitalizations |
These results show how far renal dialysis technology has come in ensuring patient safety, efficiency, and long-term sustainability.
Home Dialysis: Empowering Patient Independence
One of the most transformative aspects of current renal dialysis technology is its move toward home-based care. Home dialysis gives patients greater control over their schedules, improves their quality of life, and reduces dependency on healthcare infrastructure. With devices becoming smaller, smarter, and more user-friendly, more patients are opting for this mode of treatment.
Additionally, healthcare professionals are trained to support remote monitoring systems where alerts can be transmitted in real time, allowing immediate assistance in emergencies. The shift is particularly significant in rural or under-resourced areas where access to dialysis centers is limited.
Challenges in Dialysis Technology Implementation
Despite the progress, challenges remain in the adoption and execution of renal dialysis technology on a global scale. Costs, limited healthcare infrastructure, electricity dependency, and the need for specialized training often hinder widespread usage. Efforts are underway to design solar-powered dialysis machines and develop microfluidic systems to address these gaps.
Moreover, patient education and lifestyle management remain components of successful dialysis. Integration with mobile health apps and continuous patient support are being increasingly deployed to combat adherence issues.
Global Trends and Future Outlook
As the global burden of chronic kidney disease (CKD) continues to rise, so does the demand for renal replacement therapies. Emerging economies are investing in affordable dialysis solutions, and global collaborations are driving technological partnerships. Artificial kidneys, implantable dialysis devices, and nanotechnology-based purification systems are currently in the development stages, aiming to eliminate the need for external dialysis.
Global Trends and Future Outlook
As the global burden of chronic kidney disease (CKD) grows, the need for renal replacement therapies is also increasing. More patients worldwide are depending on dialysis due to rising cases of kidney failure. Emerging economies are now prioritizing affordable and scalable dialysis technologies. Governments and private sectors are joining forces to improve dialysis accessibility. Global partnerships are accelerating innovation in renal care solutions. Artificial kidneys and implantable dialysis devices are under active research. Nanotechnology-based purification systems are also showing promising results. These advancements may eventually remove the need for traditional external dialysis.
Miniaturization of Machines
Dialysis machines are being redesigned to become smaller, more portable, and easier to operate at home or on the move. This trend enhances treatment flexibility for patients who wish to avoid frequent hospital visits. Despite their compact size, these machines still provide reliable, high-quality performance. Their convenience supports improved patient adherence and lifestyle balance.
Wireless Patient Monitoring
Using smart sensors and network connectivity, modern dialysis systems can send real-time patient data to medical professionals. This supports continuous monitoring, immediate alerts, and data-driven decision-making. Patients feel more secure knowing they are being monitored even from home. It’s especially beneficial in cases where rapid intervention is needed.
AI-Integrated Personalized Dialysis
Artificial Intelligence in dialysis helps tailor treatment sessions to individual needs by analyzing a patient’s history and real-time vitals. These systems adjust filtration speed, fluid removal, and pressure settings automatically. It reduces the risk of side effects and enhances safety. Personalized dialysis ensures optimal efficiency and long-term health management.
Telemedicine-Supported Dialysis Services
Telemedicine is expanding access to nephrology expertise through virtual care. Patients in remote or underserved areas can now consult with doctors without leaving their homes. Follow-ups, training, and troubleshooting can also be managed online. This trend minimizes travel and strengthens continuity of care across locations.
Eco-Friendly Consumables and Recyclable Filters
Sustainable practices are becoming a priority in dialysis technology. Manufacturers are producing recyclable dialyzers, biodegradable tubing, and water-saving machines. These innovations reduce the environmental burden without compromising treatment quality. The goal is to provide responsible renal care that supports both human health and the planet.
Wrapping Up
Renal dialysis technology continues to break barriers in how chronic kidney disease is managed globally. Its role has shifted from being a life-saving measure to a quality-of-life enhancer. Newer machines are smarter, faster, and more responsive to patient needs. Patients can now enjoy greater flexibility with home-based and wearable dialysis devices. Healthcare systems are also adapting with remote monitoring and AI-driven platforms. The increasing need for individualized care has spurred innovations.
From fluid control to infection prevention, technology is tackling every angle. Affordability and accessibility remain ongoing challenges in many regions. Yet, continuous innovation is closing these gaps at a rapid pace. Future developments like implantable artificial kidneys hold exciting possibilities. As we move ahead, renal dialysis will likely become more preventive and seamless. Ultimately, it offers patients not just survival but a better way to live..
FAQs
What is renal dialysis technology used for?
Renal dialysis technology is designed to support individuals with severe kidney failure or end-stage renal disease. It replaces the natural filtering function of the kidneys by removing toxins, excess fluids, and waste from the blood. This process helps maintain electrolyte balance and prevents complications related to kidney dysfunction. It is for patients awaiting kidney transplants or those who are not transplant candidates.
What are the main types of renal dialysis technologies available today?
The primary types include hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and home-based solutions like home hemodialysis and nocturnal dialysis. Hemodialysis involves external filtering using a dialyzer, while peritoneal dialysis uses the body’s peritoneal membrane. Home dialysis allows for flexible scheduling and greater patient independence. These technologies cater to various lifestyles, clinical conditions, and levels of care.
How has modern technology improved dialysis treatment outcomes?
Technological innovations have significantly improved renal dialysis treatments through automation, portability, and data-driven personalization. Smart dialysis machines can now monitor blood pressure, fluid levels, and waste concentration in real-time. AI integration helps in customizing treatments to minimize side effects. These developments have led to improved survival rates and a better quality of life for patients.
Is it safe and practical to perform dialysis at home?
Yes, with advancements in compact dialysis machines and remote monitoring technologies, home dialysis is both safe and effective. Patients receive thorough training and support from healthcare providers. Emergency alert systems and telemedicine services provide real-time assistance if needed. Home-based options also reduce the need for frequent hospital visits and offer greater scheduling flexibility.
What future advancements are expected in renal dialysis technology?
Future developments include implantable artificial kidneys, nanotechnology-based filters, and wearable dialysis devices. Researchers are also working on fully automated systems that require minimal human intervention. These innovations aim to reduce treatment time, lower healthcare costs, and eliminate the dependency on external dialysis units. The ultimate goal is to make kidney support more natural, accessible, and patient-centric.
How do wearable and portable dialysis devices benefit patients?
Wearable and portable dialysis technologies allow patients to move freely and manage treatments on the go. These compact machines are designed for travel, work, and home use, improving lifestyle compatibility. They also reduce the time spent at clinics and encourage better treatment adherence. Such devices promote independence and help patients maintain a sense of normalcy in their daily lives.
What challenges still exist in global dialysis accessibility and affordability?
Despite progress, many regions still face issues with dialysis access due to infrastructure gaps, high costs, and limited trained personnel. Emerging technologies aim to address these issues by introducing solar-powered machines and low-cost systems. Global partnerships and healthcare investments are to bridge this gap. Expanding training and outreach programs can also help improve adoption and delivery worldwide.